GraphQL은 N+1 문제를 어떻게 해결했을까? (w/ dataloader)
11 min read
GraphQL에서의 N+1 문제 알아보기
N+1 문제란?
N+1은 관계형 데이터를 조회할 때 발생할 수 있는 대표적인 성능 ��이슈이다.
이름에서 알 수 있듯이 하나의 쿼리 이후 N개의 추가 쿼리가 발생하는 패턴을 의미하는데..
코드로 보는게 이해가 가장 빠를 것 같다..! 😂
간단한 환경을 구성해서 직접 확인해보자. (관련 코드)
다음 라이브러리들을 설치한다.
package.json
pnpm i @apollo/server better-sqlite3 graphql graphql-tagindex.js
import { ApolloServer } from '@apollo/server'
import { startStandaloneServer } from '@apollo/server/standalone'
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
import db from './database.js'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
comments: [Comment!]!
}
type Comment {
id: ID!
content: String!
post: Post!
}
type Query {
posts: [Post!]!
post(id: ID!): Post
}
`
const resolvers = {
Query: {
posts: () => {
console.log('Fetching all posts')
return db.prepare('SELECT * FROM posts').all()
},
},
Post: {
comments: (post) => {
console.log(`Fetching comments for post ${post.id}`)
return db.prepare('SELECT * FROM comments WHERE post_id = ?').all(post.id)
},
},
}
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
})
const { url } = await startStandaloneServer(server, {
listen: { port: 4001 },
})
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at: ${url}`)database.js
import { existsSync } from 'node:fs'
import Database from 'better-sqlite3'
const dbPath = 'blog.db'
const db = new Database(dbPath)
if (!existsSync(dbPath)) {
db.exec(`
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS posts;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS comments;
CREATE TABLE posts (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT,
content TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE comments (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
post_id INTEGER,
content TEXT,
FOREIGN KEY (post_id) REFERENCES posts (id)
);
-- 샘플 데이터 삽입
INSERT INTO posts (title, content) VALUES
('첫 번째 글', '안녕하세요'),
('두 번째 글', '반갑습니다'),
('세 번째 글', '날씨가 좋네요');
INSERT INTO comments (post_id, content) VALUES
(1, '좋은 글이에요!'),
(1, '감사합니다'),
(2, '동의합니다'),
(3, '멋진 글이네요'),
(3, '잘 보고 갑니다');
`)
}
export default dbOperation
posts 내 comments를 불러온다.
query {
posts {
id
title
comments {
id
content
}
}
}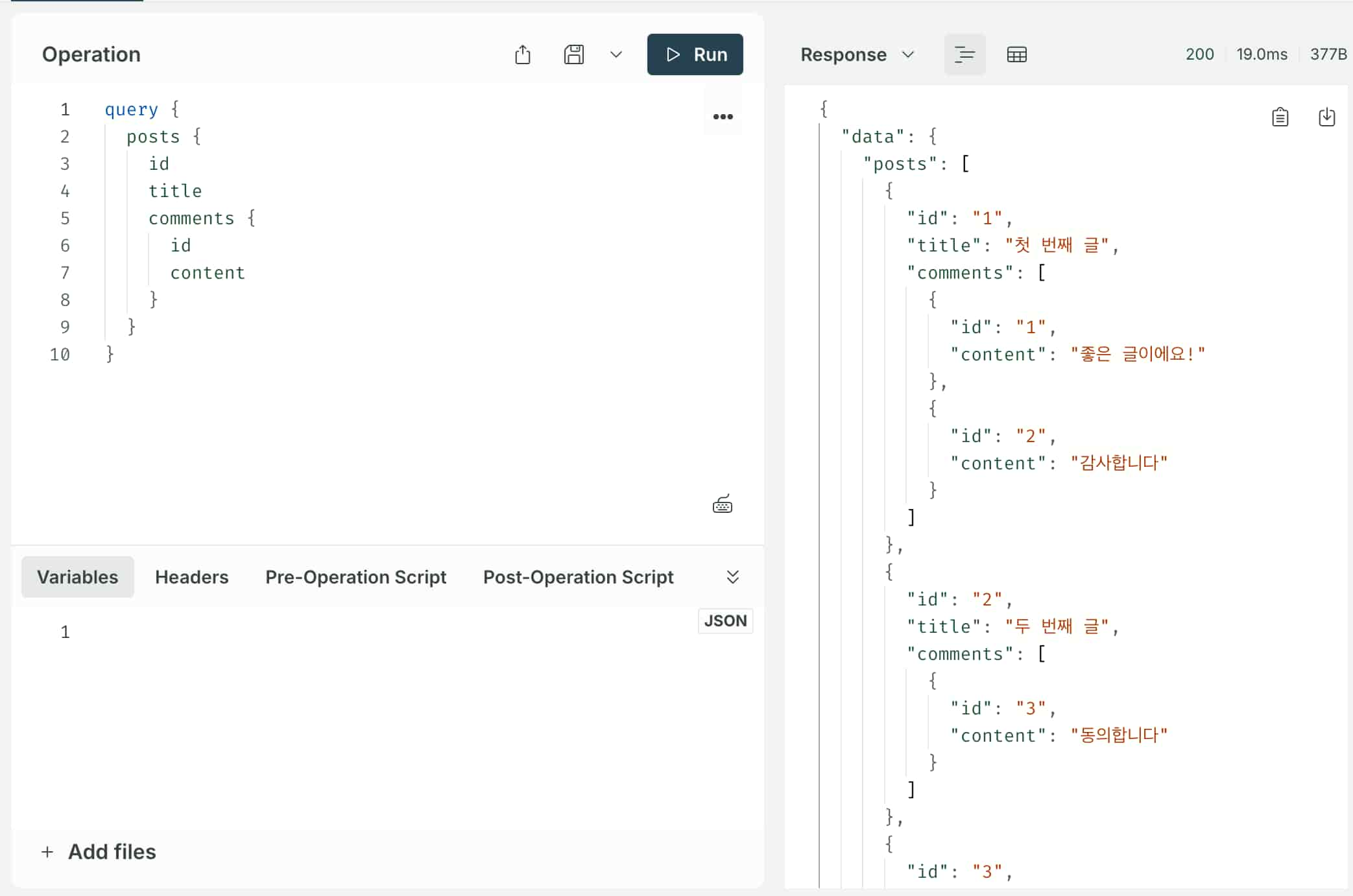
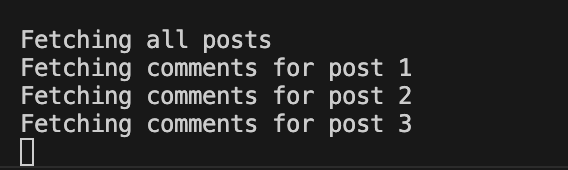
결과
4번의 호출(N+1)이 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
dataloader
이러한 N+1 문제를 해결하기 위해 GraphQL은 dataloader라는 도구를 활용한다.
dataloader를 설치한다.
pnpm i dataloaderindex-dataloader.js
import { ApolloServer } from '@apollo/server'
import { startStandaloneServer } from '@apollo/server/standalone'
import DataLoader from 'dataloader'
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
import db from './database.js'
const typeDefs = gql`
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String!
content: String!
comments: [Comment!]!
}
type Comment {
id: ID!
content: String!
post: Post!
}
type Query {
posts: [Post!]!
post(id: ID!): Post
}
`
// Comments를 배치로 로딩하는 DataLoader 생성
function createCommentsLoader() {
return new DataLoader(async (postIds) => {
console.log(`Batch loading comments for posts: ${postIds.join(', ')}`)
const comments = db
.prepare(
`SELECT * FROM comments WHERE post_id IN (${postIds.map(() => '?').join(',')})`,
)
.all(...postIds)
// postId별로 comments 그룹화하여 반환
return postIds.map((postId) =>
comments.filter((comment) => comment.post_id === Number.parseInt(postId)),
)
})
}
const resolvers = {
Query: {
posts: () => {
console.log('Fetching all posts')
return db.prepare('SELECT * FROM posts').all()
},
},
Post: {
comments: (post, _, context) => {
return context.commentsLoader.load(post.id)
},
},
}
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers })
const { url } = await startStandaloneServer(server, {
listen: { port: 4000 },
context: () => ({
commentsLoader: createCommentsLoader(),
}),
})
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at: ${url}`)Operation
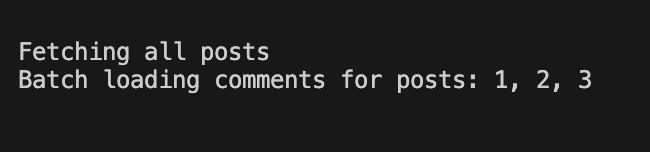
동일한 쿼리를 호출한다.
결과
이전과 달리 2번의 호출만 발생한다.
어떻게 이러한 동작이 가능해진걸까?
내부 코드 분석
dataloder는 약 500줄로 이루어진 라이브러리다.
내부 코드를 살펴보면 배칭과 캐싱 기능이 적용되는데,
이번 글에서는 캐싱과 관련된 내용은 다루지 않고 배칭에 대해서만 알아보고자 한다.
batching
여러 개별 데이터 요청을 단일 요청으로 모아서 처리한다.
이를 통해 네트워크 왕복을 줄이고 성능을 개선시키고자 한다.
크게 다음 코드들을 핵심으로 잡고 살펴볼 것이다.
임의로 생략한 부분들이 많기에 참고하시길..😇 (원본 코드)
주요 타입 정의
// 배치 로딩 함수 타입 - 키 배열을 받아 Promise 배열 반환
export type BatchLoadFn<K, V> = (keys: Array<K>) => Promise<Array<V | Error>>
// 배치 관련 옵션
export type Options<K, V, C = K> = {
batch?: boolean // 배칭 활성화 여부
maxBatchSize?: number // 최대 배치 크기
batchScheduleFn?: (callback: () => void) => void // 배치 실행 스케줄러
// 기타 캐싱 관련 옵션들...
}
// 배치 상태 추적 구조
type Batch<K, V> = {
hasDispatched: boolean // 처리 상태
keys: Array<K> // 수집된 키들
callbacks: Array<{
// 각 키별 콜백
resolve: (value: V) => void
reject: (error: Error) => void
}>
cacheHits?: Array<() => void> // 캐시 동작 콜백
}BatchLoadFn 타입은 dataloader의 핵심 함수 타입이다.
여러 개의 키를 한 번에 처리하고자 사용된다.
예제에서는 createCommentsLoader 내 DataLoader로 넘긴 함수 부분이다.
예시 코드
function createCommentsLoader() {
return new DataLoader(async (postIds) => {
console.log(`Batch loading comments for posts: ${postIds.join(', ')}`)
const comments = db
.prepare(
`SELECT * FROM comments WHERE post_id IN (${postIds.map(() => '?').join(',')})`,
)
.all(...postIds)
// postId별로 comments 그룹화하여 반환
return postIds.map((postId) =>
comments.filter((comment) => comment.post_id === Number.parseInt(postId)),
)
})
}Batch 타입에서는 현재 진행 중인 배치의 상태 구조를 표현한다.
hasDispatched: 이 배치가 이미 처리됐는지 여부를 표시keys: 이 배치에 수집된 모든 키의 배열callbacks: 각 키에 대응하는 비동기 함수 배열
DataLoader 클래스
class DataLoader<K, V, C = K> {
constructor(batchLoadFn: BatchLoadFn<K, V>, options?: Options<K, V, C>) {
this._batchLoadFn = batchLoadFn;
this._maxBatchSize = getValidMaxBatchSize(options);
this._batchScheduleFn = getValidBatchScheduleFn(options);
this._batch = null;
// 기타 초기화...
}
_batchLoadFn: BatchLoadFn<K, V>; // 사용처에 제공되는 배치 로드 함수
_maxBatchSize: number; // 최대 배치 크기
_batchScheduleFn: (() => void) => void; // 배치 스케줄링 함수
_batch: Batch<K, V> | null; // 현재 활성 배치
// 기타 필드들...
load(key: K): Promise<V> {
if (key === null || key === undefined) {
throw new TypeError(
'The loader.load() function must be called with a value, ' +
`but got: ${String(key)}.`,
);
}
const batch = getCurrentBatch(this); // 현재 배치 가져오기
// 캐시 체크 코드 생략...
batch.keys.push(key); // 배치에 키 추가
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
batch.callbacks.push({ resolve, reject });
});
// 캐시 저장 코드 생략...
return promise;
}
}DataLoader 클래스를 통해 배치 로딩 기능의 인터페이스를 파악할 수 있다.
_batchScheduleFn는 배치 처리 시점을 결정하는 함수이다.
이 함수를 통해 언제 배치를 실행할지 제어한다.
밑에 살펴보겠지만 해당 함수에는 enqueuePostPromiseJob 함수가 사용된다.
load 메서드에서는 하나의 키에 대한 데이터 로드를 요청한다.
내부적으로 getCurrentBatch 함수를 통해 현재 활성화된 배치를 가져온다.
가져온 배치에서 keys, callbacks 배열에 키와 함수를 추가한다.
- 처음
load호출 시 새 배치 생성 - 같은 이벤트 루프
tick내 후속load호출은 동일 배치에 누적 - 배치가 이미 처리 중이거나 최대 크기에 도달하면 새 배치 생성
배치 관리 핵심 함수들
// 현재 배치 가져오기 또는 새 배치 생성
function getCurrentBatch<K, V>(loader: DataLoader<K, V, any>): Batch<K, V> {
const existingBatch = loader._batch
// 재사용 가능한 배치가 있으면 사용
if (
existingBatch !== null &&
!existingBatch.hasDispatched &&
existingBatch.keys.length < loader._maxBatchSize
) {
return existingBatch
}
// 새 배치 생성
const newBatch = { hasDispatched: false, keys: [], callbacks: [] }
loader._batch = newBatch
// 이벤트 루프의 다음 틱에 배치 처리 예약
loader._batchScheduleFn(() => {
dispatchBatch(loader, newBatch)
})
return newBatch
}
// 배치 실행 함수
function dispatchBatch<K, V>(loader: DataLoader<K, V, any>, batch: Batch<K, V>) {
// 배치 상태 업데이트
batch.hasDispatched = true
// 빈 배치는 바로 종료
if (batch.keys.length === 0) return
// 사용자 정의 배치 함수 호출
let batchPromise
try {
batchPromise = loader._batchLoadFn(batch.keys)
} catch (e) {
// 에러 처리...
}
// 기타 에러 처리...
// 결과 처리
batchPromise
.then((values) => {
// 각 키에 대한 결과 분배
for (let i = 0; i < batch.callbacks.length; i++) {
const value = values[i]
if (value instanceof Error) {
batch.callbacks[i].reject(value)
} else {
batch.callbacks[i].resolve(value)
}
}
})
.catch((error) => {
failedDispatch(loader, batch, error)
})
}_batchScheduleFn이 이해하기 까다로웠는데 핵심 부분이라고 생각된다..! 🧐
_batchScheduleFn의 호출 시점은 다음과 같다.
getCurrentBatch가 새로운 배치를 생성할 때마다 호출- 보통 한 이벤트 루프
tick내에서 첫 번째load호출 시에만 발생 - 배치가 이미 존재하고 재사용 가능하면 호출되지 않음
dispatchBatch는 앞서 load 메서드에서 구성한 keys, callbacks에 대한 처리가 이루어진다고 보면 될 것 같다.
배치 스케줄��링 메커니즘
// 배치 스케줄링 함수 검증
function getValidBatchScheduleFn(options): (() => void) => void {
// 옵션에 명시되지 않았으면 기본값 사용
if (!options || options.batchScheduleFn === undefined) {
return enqueuePostPromiseJob;
}
return options.batchScheduleFn;
}
// 환경에 따른 스케줄링 선택
const enqueuePostPromiseJob =
// Node.js 환경
typeof process === 'object' && typeof process.nextTick === 'function'
? function(fn) {
Promise.resolve().then(() => process.nextTick(fn));
}
// setImmediate 지원 환경
: typeof setImmediate === 'function'
? function(fn) {
setImmediate(fn);
}
// 기타 환경
: function(fn) {
setTimeout(fn);
};getValidBatchScheduleFn은 초기화 과정에서 _batchScheduleFn에 사용되는 함수이다.
(_batchScheduleFn은 getCurrentBatch 함수 내부에서 사용된다.)
일반적으로 enqueuePostPromiseJob을 사용하게 된다.
여기에서의 비동기 동작으로 load에서 수집한 동작을 한 번에 처리할 수 있게 해준다.
process.nextTick
처음 접한 코드여서 추가로 정리해본다. 😅
Node.js 이벤트 루프에서 제공하는 비동기 실행 메커니즘이다.
process.nextTick에 함수를 전달하면 이벤트 루프에서 현재 실행 코드가 완료된 직후,
다음 단계로 이동하기 전에 함수를 실행하도록 지시한다.
It's the way we can tell the JS engine to process a function asynchronously (after the current function), but as soon as possible, not queue it.
JS 엔진에 함수를 대기열에 넣지 않고 가능한 빠르게 비동기적으로 처리할 수 있는 방법이라고 한다.
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout 콜백')
}, 0)
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('setImmediate 콜백')
})
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('nextTick 콜백')
})
console.log('동기 코드')
// 동기 코드
// nextTick 콜백
// setImmediate 콜백
// setTimeout 콜백